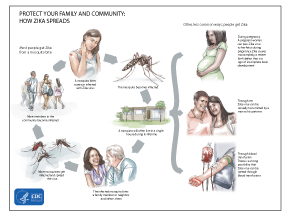
Zika Transmission
The Zika virus is mainly transmitted by mosquitoes. People are the disease reservoir, meaning mosquitoes get Zika from an infected person during the first week of their symptoms. Mosquitoes can then spread the disease to other people through bites. There are three primary methods of Zika transmission: mosquito bite, mother to baby, and sexual transmission.

Mosquito Bites
Zika spreads when a mosquito bites a person infected with Zika virus. The mosquito becomes infected with Zika virus and after a few days that mosquito will infect other people through biting. As more people become infected more mosquitoes become infected and continue to spread the virus.
Zika virus is primarily transmitted to people through the bite of an infected Aedes aegypti mosquito or possibly by an infected Aedes albopictus mosquito. These mosquitoes also transmit dengue and chikungunya virus. There have been travel-related cases of Zika in Missouri, but there have been no cases of Zika locally transmitted by a mosquito bite.
- Some Aedes prefer to bite people, can live indoors and bite during the daytime. Other Aedes also bite at night. They typically lay eggs in and near standing water in things like buckets, bowls, animal dishes, flower pots and vases.
- Mosquitoes become infected when they feed on a person already infected with the virus. Infected mosquitoes can then spread the virus to other people through bites.
From Mother to Child
- Zika virus at any stage of pregnancy may cause severe fetal brain birth defects.
- To date, Zika virus has not been shown to be passed to infants through breastfeeding.
Protect Your Family and Community:
How Zika Spreads
Through Sexual Contact
Zika virus can be spread from a person who has Zika to his or her sex partners. In known cases of sexual transmission, the virus can be spread when the person has symptoms, before symptoms start, and after symptoms resolve. Recent evidence indicates that Zika virus may also be transmitted from an infected person to his/her sex partner even if the infected individual never showed any symptoms of Zika. Zika virus is present in semen longer than other body fluids, such as vaginal fluids, urine, and blood. To effectively protect against sexual transmission of Zika, condoms must be used correctly from start to finish, every time during sex.
