Pregnancy-Associated Mortality Review (PAMR)
The Pregnancy-Associated Mortality Review program is designed to improve data collection and reporting of maternal deaths in Missouri. The PAMR board is comprised of a diverse list of health care experts and reviews all maternal deaths that occur while a woman is pregnant, or within one year of the end of her pregnancy.
Goal: to reduce preventable maternal mortality in Missouri
The PAMR board and program exist to better understand the factors that contribute to or cause maternal deaths, and prevent future occurrences through recommendations made by the PAMR board.
Key Insights (fact sheet)
- Annually, an average of 70 Missouri women die while pregnant or within one year of pregnancy.
- 80% of pregnancy-related deaths were determined to be preventable.
- Mental health conditions were the lead underlying cause of pregnancy-related deaths, followed by
cardiovascular disease.
Improving data collection and dissemination
The PAMR program prioritized data gathering and dissemination, resulting in a first-of-its-kind interactive dashboard.
Key Definitions
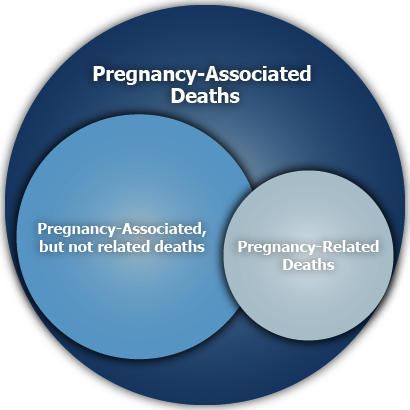
The PAMR board analyzes all maternal deaths that occur while a woman is pregnant, or within one year of the end of pregnancy. Those cases are considered pregnancy-associated deaths, but not all are determined to be pregnancy-related deaths.
Maternal Mortality
The PAMR program uses the term maternal mortality to encompass the topic of deaths during pregnancy, childbirth, and the postpartum period up to 365 days from the end of pregnancy.
Maternal Death
The death of a woman while pregnant or within 42 days of termination of pregnancy, regardless of the duration and the site of the pregnancy, from any cause related to or aggravated by the pregnancy or its management, but not from accidental causes. This definition is used by the National Center for Health Statistics and the World Health Organization.
Implementation and Improvement
The PAMR program has continued to work toward the improvement of data gathering and dissemination. To that end, the program has worked to expand the identification techniques used to enhance case identification. Additionally, the program has greatly increased its dissemination capabilities through fostering partnerships and expanding tools available for this task, such as the development of an interactive data dashboard. The program has also worked with partners to improve timeliness and to enhance the information available to the board through the abstraction process, particularly with regard to SDOH.
Summary of Major Accomplishments
The following accomplishments occurred in 2022 and the first half of 2023:
- Expanded PAMR case identification techniques to be more comprehensive and improve timeliness of case identification.
- Developed and published a public data dashboard reporting on pregnancy-associated deaths.
- Completed 44 different dissemination activities on maternal mortality, including dissemination of an infographic through social media on Jan. 23 to mark Maternal Health Awareness Day.
- Presented a poster of PAMR data at PQC conventioning and presented at the annual Association of Maternal and Child Health Programs conference titled "Polysubstance Abuse: A Pervasive Threat to Maternal Health in Missouri".
- Continued contracting with the Missouri Hospital Association on maternal mortality prevention efforts, including caring for the mother-baby dyad affected by substance use, severe hypertension in pregnancy and obstetric hemorrhage.
- Shared aggregate PAMR data as part of CDC’s Pregnancy-Related Deaths: Data from Maternal Mortality Review Committees in 36 US States, 2017-2019 brief.
Definitions
Maternal death: The death of a woman while pregnant or within 42 days of termination of pregnancy, regardless of the duration and the site of the pregnancy, from any cause related to or aggravated by the pregnancy or its management, but not from accidental causes. This definition is used by the National Center for Health Statistics and the World Health Organization.
Pregnancy-associated death (PA): A death during or within one year of pregnancy, regardless of the cause. These deaths make up the universe of maternal mortality; within that universe are pregnancy-related deaths and pregnancy-associated, but not related deaths.
Pregnancy-related death (PR): A death during or within one year of pregnancy, from a pregnancy complication, a chain of events initiated by pregnancy, or the aggravation of an unrelated condition by the physiologic effects of pregnancy.
Pregnancy-associated, but not related death (PANR): A death during or within one year of pregnancy, from a cause that is not related to pregnancy.
Maternal Mortality: The PAMR program uses the term maternal mortality to encompass the topic of deaths during pregnancy, childbirth, and the postpartum period up to 365 days from the end of pregnancy.
Alliance for Innovation on Maternal Health (AIM): Quality improvement practice/ initiative to support best practices for maternal health.
Amniotic fluid embolism (AFE): Amniotic fluids enter the mother's bloodstream during or after labor, causing an allergic-like reaction.
Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System (BRFSS): A telephone survey that collects information on health conditions, behaviors, preventative practices, and access to health care. This information helps to inform the health in our state.
Cardiovascular disorders associated with pregnancy:
- Cardiomyopathy: A condition that causes the heart to have a harder time pumping blood to the rest of the body, which can lead to symptoms of heart failure. −
- Chronic hypertension: High blood pressure present before pregnancy or diagnosed before 20 weeks of pregnancy.
- Hypertensive disorders of pregnancy: Chronic hypertension, gestational hypertension, preeclampsia, eclampsia and HELLP Syndrome (Hemolysis Elevated Liver enzymes and Low Platelet count). See definitions below.
- Eclampsia: A complication developed from preeclampsia that can cause seizures. This is a medical emergency.
- Gestational hypertension: High blood pressure that develops after 20 weeks of gestation with no other symptoms (i.e., two separate readings of blood pressure being 140/90 four hours apart, after a blood pressure reading that was within the normal range prior to).
- Preeclampsia: A complication of pregnancy that can occur after 20 weeks of pregnancy when a woman whose blood pressure had been normal suddenly develops high blood pressure and protein in the urine or other problems.
- Preeclampsia superimposed on chronic hypertension: New-onset proteinuria (protein in the urine) in a woman with high blood pressure but no proteinuria before twenty weeks gestation.
Community violence intervention (CVI): Ways to reduce homicides in communities at risk. For more information visit this website https://www.ojp.gov/topics/community-violence-intervention.
Community-based organization (CBO): Local organization, usually a nonprofit but not always, that provides services to address community needs.
Congenital anomaly: Structural (how the body is built) or functional (how the body works) birth differences that occur during fetal development.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC): Federal agency that helps conduct and support health promotion, prevention and preparedness.
County size: County size is used to show the residency not the location of death. For example, if a mom died of heart issues out of state, her case is included in the Missouri county where she lived. − Micropolitan counties/areas: Areas that contain an urban cluster of at least 10,0000 but fewer than 50,000 people. − Metropolitan counties/areas: Areas that contain an urban core of 50,000 people or more. − Rural: Counties that are not metro or micro.
Diabetes: A condition that occurs when the body cannot produce enough insulin or use the insulin in the body to remove sugar from the blood. − Gestational diabetes: A type of diabetes that develops during pregnancy. It often goes away after delivery. − Type 1 diabetes: A type of diabetes caused by an autoimmune disease that destroys insulin-producing (islet) cells in the pancreas. With this type, there is not enough insulin in the body to remove sugar from the blood. − Type 2 diabetes: A type of diabetes that occurs when the body has insulin, but does not use it properly.
Disaggregated: Separated or broken down. In this report, it is used to describe when data is provided in more detail.
Embolism (thrombotic): A critical health condition caused by a blood clot moving through the blood and getting stuck in an organ, leading to no blood flow to that area.
Funders to improve maternal health:
- Philanthropic funder: A person/organization seeking to promote the welfare of others by donating money for good causes.
- State funding: Funding or grants available through state funds that can assist with projects to improve maternal mortality.
- Federal funding: Funding or grants available through federal funds to assist with projects to improve maternal mortality.
- Other funds: Funds that are aside from philanthropic, state and federal.
Gastrointestinal (GI) disorder: Conditions that affect the GI tract, a series of hollow organs that run from the mouth to the anus.
Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA): An act to protect individuals, among other things, from being identified by medical records or individually identifiable information.
Hypertension: A condition when the pressure inside of blood vessels is too high. High blood pressure is like too much water flowing through a garden hose. The high-pressure stream ultimately damages the hose and plants it sprays.
Hemorrhage: Heavy bleeding.
Homicide: Killing of one person by another person.
Infection
- Sepsis/septic shock: This is caused by chemicals that are released in the bloodstream to fight an infection that trigger inflammation throughout the body.
- COVID-19: A disease caused by a virus named SARS-CoV-2. It can be very contagious and spreads quickly. In this report, when COVID-19 is listed as a cause of death, this means they were diagnosed with the infection and it led to their death.
Intimate Partner Violence (IPV) also known as DV (Domestic Violence): A pattern of behavior in any relationship that is used to gain or maintain power and control over an intimate partner. Abuse may be physical, sexual, emotional, economic or psychological actions or threats of actions that influence another person.
Mental health:
- Anxiety disorder: Condition where a person can have frequent intense, and excessive worry and fear about everyday situations.
- Depressive disorder: Condition that causes a decrease in mood, or loss of interest in activities for longer periods of time.
- Perinatal mood and anxiety disorder (PMAD): Term used to describe mental health conditions experienced during pregnancy or after having a new baby, adopting or experiencing pregnancy/infant loss.
- Psychotic disorder: Mental health condition characterized by a disconnection from reality.
Maternal mortality: The death of a woman during pregnancy, childbirth and postpartum period up to 365 days from the end of pregnancy.
Maternal morbidity: Any health condition attributed to and/or aggravated by pregnancy and childbirth that negatively impacts women’s health short-term or long-term.
Naloxone: A medication to rapidly reverse an opioid overdose.
National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS): A part of the CDC that gathers, looks at and shares U.S. health information that is up-to-date, important and accurate.
Obesity: A body mass index (BMI) of 30 or higher. BMI is not valid during pregnancy. BMI values are calculated based on pre-pregnancy weight.
Opioids: A class of drugs used to reduce moderate to severe pain (i.e. heroin, morphine and oxycodone).
Opioid use disorder (OUD): A mental health condition in which a problematic pattern of opioid use creates impairment to one’s mental and physical health and causes distress and/or impairs daily life.
Overdose: A critical health state that occurs when a person takes too much of a substance, a blend of substances or medicine.
Peripartum: Time frame shortly before, during and immediately after delivering a baby.
Perinatal Quality Collaborative (PQC): Group of clinical team members and public health leaders across a state working to bring awareness and quality care to mothers, families and their babies.
Pulmonary conditions: Conditions including asthma, COPD, and other lung infections like COVID-19 that affect the ability of one's lungs to work properly.
Pregnancy-associated death: When a Missouri resident dies while pregnant, during delivery or within one year postpartum, regardless of the cause. Pregnancy-associated deaths can be further placed into one of three categories:
- Pregnancy-related death: The death of a woman that occurs during or within one year of pregnancy, from a pregnancy complication, a chain of events initiated by pregnancy, or the aggravation of an unrelated condition by the physiological effects of pregnancy.
- Pregnancy-associated, but not related death (PANR): The death of a woman during or within one year of pregnancy, from a cause that is not related to pregnancy (i.e., a pregnant woman dies in an earthquake).
- Pregnancy-associated but unable to determine relatedness: Instances when the PAMR board was unable to determine if a death was pregnancy-related or PANR. This category was counted as a PANR death in previous reports due to the small population size. For the sake of brevity, this is referred to as Unable to Determine in the charts and figures in the report.
Pregnancy-Associated Mortality Review (PAMR) Board: A group of individuals from across the state who review every pregnancy-associated death and provide recommendations to prevent future deaths.
Pregnancy-related mortality ratio (PRMR): A ratio is another way to show a fraction. It tells how many of one condition compared to the larger group. The PRMR is a fraction used to show the number of pregnancy-related deaths compared to all live births per 100,000 live births.
PRMR = (pregnancy related deaths)\(live births) x 100,000
Screening, Brief Intervention, Referral and Treatment (SBIRT): A tool used to identify individuals at risk for a condition (usually the use of substances like tobacco or alcohol) and then provide access to specialty care.
Social determinants/drivers of health (SDOH): Non-medical factors that affect health outcomes and quality of life. These factors are known as Social Determinants of Health (SDOH) or are sometimes called social drivers of health. Health isn't just about going to the doctor. They include things like not having enough money, living in unsafe or unstable housing, or being in a neighborhood that has more crime. People in areas with poor SDOH often have worse health. Improving these conditions helps everyone be healthier and reduce health differences between groups.
Severe maternal morbidity (SMM): A group of 15 unplanned negative outcomes during childbirth designated by the CDC, which can cause shortterm or long-term problems to a woman’s health.
Statistical significance: Term used to describe a test used to look at the relationship between two variables. It is performed to determine whether the difference between the two variables is the result of chance or if it is meaningful and did not happen because of chance. For this report, all tests were performed to the 95% confidence level. This means that there is 95% confidence that the relationship between the two variables was meaningful. This does not mean that one thing caused another. Without more advanced tests, it cannot be known if there is a true cause-and-effect relationship.
Substance use disorder (SUD): Recurrent use of substances such as alcohol, marijuana, methamphetamine, narcotics, etc. that causes impairment to one’s mental and physical health and causes distress and/or impairs daily life.
Surveillance: One of the steps in public health that seeks to see if there is a public health problem, and if so, what the problem is. In this report, surveillance is the step used to see what problems exist in maternal health. When timing is mentioned for surveillance, it states what time frame we look at to identify the problem.
Unreliable ratio: A ratio is another way to show a fraction. It tells how often a condition occurs within a larger group. Ratios based on numbers smaller than 25 are unreliable. This is because they are easily influenced by small changes in how often a condition occurs. To improve the dependability of report findings, analysts combine numbers from different variables. In this report, analysts often combined five years of data to obtain the most reliable ratios possible. Figures where the calculated ratio are unreliable are indicated using hashed bars on the graphs.
Pregnancy Resources for Moms
DHSS Links
Department of Social Services Links
Federal Links
Additional Links
Resources for Providers
Partner Links
- MHA: Maternal-Child Health
- Missouri Perinatal Quality Collaborative (MO PQC)
- Baby and Me Tobacco Free
- Alliance for Innovation on Maternal Health (AIM)
- California Maternal Quality Care Collaborative (CMQCC)
- Cardiovascular Disease in Pregnant and Postpartum Women
- CVD Assessment Algorithm
- B-Type Natriuretic Peptide (BNP)
- Maternal Risks for Underlying Cardiovascular Disease: Key Consensus Tables
- Resources When Caring for Women with Adult Congenital Heart Disease or Other Forms of Cardiovascular Disease
- Guide to Cardiovascular Disease Medications for Pregnancy and Breastfeeding Women
- Guide to Contraception Information for Women with Cardiovascular Disease
Federal Links
Video: A Physician Shares Stories about Listening to Black Women